# [SheetJS js-xlsx](http://sheetjs.com)
Parser and writer for various spreadsheet formats. Pure-JS cleanroom
implementation from official specifications, related documents, and test files.
Emphasis on parsing and writing robustness, cross-format feature compatibility
with a unified JS representation, and ES3/ES5 browser compatibility back to IE6.
This is the community version. We also offer a pro version with performance
enhancements, additional features by request, and dedicated support.
[**Pro Version**](http://sheetjs.com/pro)
[**Commercial Support**](http://sheetjs.com/support)
[**Rendered Documentation**](http://docs.sheetjs.com/)
[**In-Browser Demos**](http://sheetjs.com/demos)
[**Source Code**](http://git.io/xlsx)
[**Issues and Bug Reports**](https://github.com/sheetjs/js-xlsx/issues)
[**Other General Support Issues**](https://discourse.sheetjs.com)
[**File format support for known spreadsheet data formats:**](#file-formats)
Graph of supported formats (click to show)
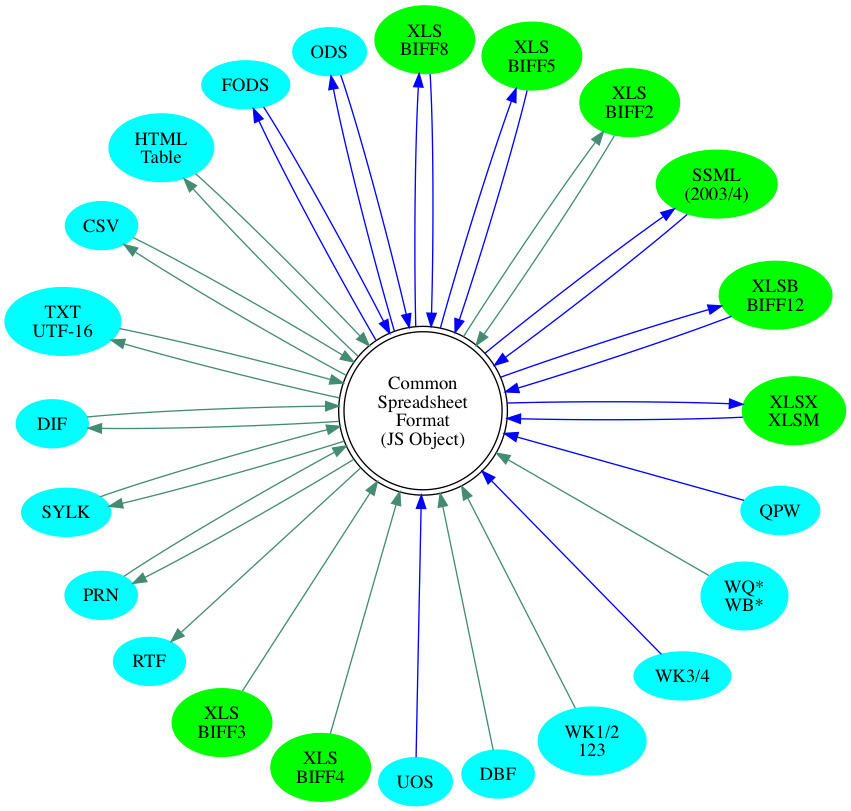
[**Browser Test**](http://oss.sheetjs.com/js-xlsx/tests/)
[](https://saucelabs.com/u/sheetjs)
[](https://travis-ci.org/SheetJS/js-xlsx)
[](https://semaphoreci.com/sheetjs/js-xlsx)
[](https://coveralls.io/r/SheetJS/js-xlsx?branch=master)
[](https://david-dm.org/sheetjs/js-xlsx)
[](https://npmjs.org/package/xlsx)
[](https://ghit.me/repo/sheetjs/js-xlsx)
[](https://github.com/SheetJS/js-xlsx)
## Table of Contents
Expand to show Table of Contents
- [Installation](#installation)
* [JS Ecosystem Demos](#js-ecosystem-demos)
* [Optional Modules](#optional-modules)
* [ECMAScript 5 Compatibility](#ecmascript-5-compatibility)
- [Philosophy](#philosophy)
- [Parsing Workbooks](#parsing-workbooks)
* [Parsing Examples](#parsing-examples)
* [Streaming Read](#streaming-read)
- [Working with the Workbook](#working-with-the-workbook)
* [Parsing and Writing Examples](#parsing-and-writing-examples)
- [Writing Workbooks](#writing-workbooks)
* [Writing Examples](#writing-examples)
* [Streaming Write](#streaming-write)
- [Interface](#interface)
* [Parsing functions](#parsing-functions)
* [Writing functions](#writing-functions)
* [Utilities](#utilities)
- [Common Spreadsheet Format](#common-spreadsheet-format)
* [General Structures](#general-structures)
* [Cell Object](#cell-object)
+ [Data Types](#data-types)
+ [Dates](#dates)
* [Sheet Objects](#sheet-objects)
+ [Worksheet Object](#worksheet-object)
+ [Chartsheet Object](#chartsheet-object)
+ [Macrosheet Object](#macrosheet-object)
+ [Dialogsheet Object](#dialogsheet-object)
* [Workbook Object](#workbook-object)
+ [Workbook File Properties](#workbook-file-properties)
* [Workbook-Level Attributes](#workbook-level-attributes)
+ [Defined Names](#defined-names)
+ [Miscellaneous Workbook Properties](#miscellaneous-workbook-properties)
* [Document Features](#document-features)
+ [Formulae](#formulae)
+ [Column Properties](#column-properties)
+ [Row Properties](#row-properties)
+ [Number Formats](#number-formats)
+ [Hyperlinks](#hyperlinks)
+ [Cell Comments](#cell-comments)
+ [Sheet Visibility](#sheet-visibility)
+ [VBA and Macros](#vba-and-macros)
- [Parsing Options](#parsing-options)
* [Input Type](#input-type)
* [Guessing File Type](#guessing-file-type)
- [Writing Options](#writing-options)
* [Supported Output Formats](#supported-output-formats)
* [Output Type](#output-type)
- [Utility Functions](#utility-functions)
* [Array of Arrays Input](#array-of-arrays-input)
* [Array of Objects Input](#array-of-objects-input)
* [HTML Table Input](#html-table-input)
* [Formulae Output](#formulae-output)
* [Delimiter-Separated Output](#delimiter-separated-output)
+ [UTF-16 Unicode Text](#utf-16-unicode-text)
* [HTML Output](#html-output)
* [JSON](#json)
- [File Formats](#file-formats)
* [Excel 2007+ XML (XLSX/XLSM)](#excel-2007-xml-xlsxxlsm)
* [Excel 2.0-95 (BIFF2/BIFF3/BIFF4/BIFF5)](#excel-20-95-biff2biff3biff4biff5)
* [Excel 97-2004 Binary (BIFF8)](#excel-97-2004-binary-biff8)
* [Excel 2003-2004 (SpreadsheetML)](#excel-2003-2004-spreadsheetml)
* [Excel 2007+ Binary (XLSB, BIFF12)](#excel-2007-binary-xlsb-biff12)
* [Delimiter-Separated Values (CSV/TXT)](#delimiter-separated-values-csvtxt)
* [Other Workbook Formats](#other-workbook-formats)
+ [Lotus 1-2-3 (WKS/WK1/WK2/WK3/WK4/123)](#lotus-1-2-3-wkswk1wk2wk3wk4123)
+ [Quattro Pro (WQ1/WQ2/WB1/WB2/WB3/QPW)](#quattro-pro-wq1wq2wb1wb2wb3qpw)
+ [OpenDocument Spreadsheet (ODS/FODS)](#opendocument-spreadsheet-odsfods)
+ [Uniform Office Spreadsheet (UOS1/2)](#uniform-office-spreadsheet-uos12)
* [Other Single-Worksheet Formats](#other-single-worksheet-formats)
+ [dBASE and Visual FoxPro (DBF)](#dbase-and-visual-foxpro-dbf)
+ [Symbolic Link (SYLK)](#symbolic-link-sylk)
+ [Lotus Formatted Text (PRN)](#lotus-formatted-text-prn)
+ [Data Interchange Format (DIF)](#data-interchange-format-dif)
+ [HTML](#html)
+ [Rich Text Format (RTF)](#rich-text-format-rtf)
- [Testing](#testing)
* [Node](#node)
* [Browser](#browser)
* [Tested Environments](#tested-environments)
* [Test Files](#test-files)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
* [OSX/Linux](#osxlinux)
* [Windows](#windows)
* [Tests](#tests)
- [License](#license)
- [References](#references)
## Installation
In the browser, just add a script tag:
```html
```
CDN Availability (click to show)
| CDN | URL |
|-----------:|:-----------------------------------------|
| `unpkg` | |
| `jsDelivr` | |
| `CDNjs` | |
`unpkg` makes the latest version available at:
```html
```
With [npm](https://www.npmjs.org/package/xlsx):
```bash
$ npm install xlsx
```
With [bower](http://bower.io/search/?q=js-xlsx):
```bash
$ bower install js-xlsx
```
### JS Ecosystem Demos
The [`demos` directory](demos/) includes sample projects for:
**Frameworks and APIs**
- [`angular 1.x`](demos/angular/)
- [`angular 2.x / 4.x`](demos/angular2/)
- [`meteor`](demos/meteor/)
- [`react and react-native`](demos/react/)
- [`vue 2.x and weex`](demos/vue/)
- [`XMLHttpRequest and fetch`](demos/xhr/)
- [`nodejs server`](demos/server/)
**Bundlers and Tooling**
- [`browserify`](demos/browserify/)
- [`requirejs`](demos/requirejs/)
- [`rollup`](demos/rollup/)
- [`systemjs`](demos/systemjs/)
- [`webpack 2.x`](demos/webpack/)
**Platforms and Integrations**
- [`electron application`](demos/electron/)
- [`nw.js application`](demos/nwjs/)
- [`Adobe ExtendScript`](demos/extendscript/)
- [`Headless Browsers`](demos/headless/)
- [`canvas-datagrid`](demos/datagrid/)
- [`Swift JSC and other engines`](demos/altjs/)
### Optional Modules
Optional features (click to show)
The node version automatically requires modules for additional features. Some
of these modules are rather large in size and are only needed in special
circumstances, so they do not ship with the core. For browser use, they must
be included directly:
```html
```
An appropriate version for each dependency is included in the dist/ directory.
The complete single-file version is generated at `dist/xlsx.full.min.js`
Webpack and Browserify builds include optional modules by default. Webpack can
be configured to remove support with `resolve.alias`:
```js
/* uncomment the lines below to remove support */
resolve: {
alias: { "./dist/cpexcel.js": "" } // <-- omit international support
}
```
### ECMAScript 5 Compatibility
Since the library uses functions like `Array#forEach`, older browsers require
[shims to provide missing functions](http://oss.sheetjs.com/js-xlsx/shim.js).
To use the shim, add the shim before the script tag that loads `xlsx.js`:
```html
```
## Philosophy
Philosophy (click to show)
Prior to SheetJS, APIs for processing spreadsheet files were format-specific.
Third-party libraries either supported one format, or they involved a separate
set of classes for each supported file type. Even though XLSB was introduced in
Excel 2007, nothing outside of SheetJS or Excel supported the format.
To promote a format-agnostic view, js-xlsx starts from a pure-JS representation
that we call the ["Common Spreadsheet Format"](#common-spreadsheet-format).
Emphasizing a uniform object representation enables new features like format
conversion (reading an XLSX template and saving as XLS) and circumvents the
"class trap". By abstracting the complexities of the various formats, tools
need not worry about the specific file type!
A simple object representation combined with careful coding practices enables
use cases in older browsers and in alternative environments like ExtendScript
and Web Workers. It is always tempting to use the latest and greatest features,
but they tend to require the latest versions of browsers, limiting usability.
Utility functions capture common use cases like generating JS objects or HTML.
Most simple operations should only require a few lines of code. More complex
operations generally should be straightforward to implement.
Excel pushes the XLSX format as default starting in Excel 2007. However, there
are other formats with more appealing properties. For example, the XLSB format
is spiritually similar to XLSX but files often tend up taking less than half the
space and open much faster! Even though an XLSX writer is available, other
format writers are available so users can take advantage of the unique
characteristics of each format.
## Parsing Workbooks
For parsing, the first step is to read the file. This involves acquiring the
data and feeding it into the library. Here are a few common scenarios:
nodejs read a file (click to show)
`readFile` is only available in server environments. Browsers have no API for
reading arbitrary files given a path, so another strategy must be used.
```js
if(typeof require !== 'undefined') XLSX = require('xlsx');
var workbook = XLSX.readFile('test.xlsx');
/* DO SOMETHING WITH workbook HERE */
```
Browser read TABLE element from page (click to show)
The `table_to_book` and `table_to_sheet` utility functions take a DOM TABLE
element and iterate through the child nodes.
```js
var worksheet = XLSX.utils.table_to_book(document.getElementById('tableau'));
/* DO SOMETHING WITH workbook HERE */
```
Alternatively, the HTML code can be extracted and parsed:
```js
var htmlstr = document.getElementById('tableau').outerHTML;
var worksheet = XLSX.read(htmlstr, {type:'string'});
```
Browser download file (ajax) (click to show)
Note: for a more complete example that works in older browsers, check the demo
at ). The directory also
includes more examples with `XMLHttpRequest` and `fetch`.
```js
var url = "http://oss.sheetjs.com/test_files/formula_stress_test.xlsx";
/* set up async GET request */
var req = new XMLHttpRequest();
req.open("GET", url, true);
req.responseType = "arraybuffer";
req.onload = function(e) {
var data = new Uint8Array(req.response);
var workbook = XLSX.read(data, {type:"array"});
/* DO SOMETHING WITH workbook HERE */
}
req.send();
```
Browser drag-and-drop (click to show)
Drag-and-drop uses the HTML5 `FileReader` API, loading the data with
`readAsBinaryString` or `readAsArrayBuffer`. Since not all browsers support the
full `FileReader` API, dynamic feature tests are highly recommended.
```js
var rABS = true; // true: readAsBinaryString ; false: readAsArrayBuffer
function handleDrop(e) {
e.stopPropagation(); e.preventDefault();
var files = e.dataTransfer.files, f = files[0];
var reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = function(e) {
var data = e.target.result;
if(!rABS) data = new Uint8Array(data);
var workbook = XLSX.read(data, {type: rABS ? 'binary' : 'array'});
/* DO SOMETHING WITH workbook HERE */
};
if(rABS) reader.readAsBinaryString(f); else reader.readAsArrayBuffer(f);
}
drop_dom_element.addEventListener('drop', handleDrop, false);
```
Browser file upload form element (click to show)
Data from file input elements can be processed using the same `FileReader` API
as in the drag-and-drop example:
```js
var rABS = true; // true: readAsBinaryString ; false: readAsArrayBuffer
function handleFile(e) {
var files = e.target.files, f = files[0];
var reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = function(e) {
var data = e.target.result;
if(!rABS) data = new Uint8Array(data);
var workbook = XLSX.read(data, {type: rABS ? 'binary' : 'array'});
/* DO SOMETHING WITH workbook HERE */
};
if(rABS) reader.readAsBinaryString(f); else reader.readAsArrayBuffer(f);
}
input_dom_element.addEventListener('change', handleFile, false);
```
### Parsing Examples
- HTML5 File API / Base64 Text / Web Workers
Note that older versions of IE do not support HTML5 File API, so the Base64 mode
is used for testing.
Get Base64 encoding on OSX / Windows (click to show)
On OSX you can get the Base64 encoding with:
```bash
$ certutil -encode target_file target_file.b64
```
(note: You have to open the file and remove the header and footer lines)
- XMLHttpRequest
### Streaming Read
Why is there no Streaming Read API? (click to show)
The most common and interesting formats (XLS, XLSX/M, XLSB, ODS) are ultimately
ZIP or CFB containers of files. Neither format puts the directory structure at
the beginning of the file: ZIP files place the Central Directory records at the
end of the logical file, while CFB files can place the storage info anywhere in
the file! As a result, to properly handle these formats, a streaming function
would have to buffer the entire file before commencing. That belies the
expectations of streaming, so we do not provide any streaming read API.
When dealing with Readable Streams, the easiest approach is to buffer the stream
and process the whole thing at the end. This can be done with a temporary file
or by explicitly concatenating the stream:
Explicitly concatenating streams (click to show)
```js
var fs = require('fs');
var XLSX = require('xlsx');
function process_RS(stream/*:ReadStream*/, cb/*:(wb:Workbook)=>void*/)/*:void*/{
var buffers = [];
stream.on('data', function(data) { buffers.push(data); });
stream.on('end', function() {
var buffer = Buffer.concat(buffers);
var workbook = XLSX.read(buffer, {type:"buffer"});
/* DO SOMETHING WITH workbook IN THE CALLBACK */
cb(workbook);
});
}
```
More robust solutions are available using modules like `concat-stream`.
Writing to filesystem first (click to show)
This example uses [`tempfile`](https://npm.im/tempfile) to generate file names:
```js
var fs = require('fs'), tempfile = require('tempfile');
var XLSX = require('xlsx');
function process_RS(stream/*:ReadStream*/, cb/*:(wb:Workbook)=>void*/)/*:void*/{
var fname = tempfile('.sheetjs');
console.log(fname);
var ostream = fs.createWriteStream(fname);
stream.pipe(ostream);
ostream.on('finish', function() {
var workbook = XLSX.readFile(fname);
fs.unlinkSync(fname);
/* DO SOMETHING WITH workbook IN THE CALLBACK */
cb(workbook);
});
}
```
## Working with the Workbook
The full object format is described later in this README.
Reading a specific cell (click to show)
This example extracts the value stored in cell A1 from the first worksheet:
```js
var first_sheet_name = workbook.SheetNames[0];
var address_of_cell = 'A1';
/* Get worksheet */
var worksheet = workbook.Sheets[first_sheet_name];
/* Find desired cell */
var desired_cell = worksheet[address_of_cell];
/* Get the value */
var desired_value = (desired_cell ? desired_cell.v : undefined);
```
Adding a new worksheet to a workbook (click to show)
This example uses [`XLSX.utils.aoa_to_sheet`](#array-of-arrays-input) to make a
worksheet and appends the new worksheet to the workbook:
```js
var new_ws_name = "SheetJS";
/* make worksheet */
var ws_data = [
[ "S", "h", "e", "e", "t", "J", "S" ],
[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]
];
var ws = XLSX.utils.aoa_to_sheet(ws_data);
/* Add the sheet name to the list */
wb.SheetNames.push(ws_name);
/* Load the worksheet object */
wb.Sheets[ws_name] = ws;
```
### Parsing and Writing Examples
- read + modify + write files
- node
The node version installs a command line tool `xlsx` which can read spreadsheet
files and output the contents in various formats. The source is available at
`xlsx.njs` in the bin directory.
Some helper functions in `XLSX.utils` generate different views of the sheets:
- `XLSX.utils.sheet_to_csv` generates CSV
- `XLSX.utils.sheet_to_html` generates HTML
- `XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json` generates an array of objects
- `XLSX.utils.sheet_to_formulae` generates a list of formulae
## Writing Workbooks
For writing, the first step is to generate output data. The helper functions
`write` and `writeFile` will produce the data in various formats suitable for
dissemination. The second step is to actual share the data with the end point.
Assuming `workbook` is a workbook object:
nodejs write a file (click to show)
`writeFile` is only available in server environments. Browsers have no API for
writing arbitrary files given a path, so another strategy must be used.
```js
if(typeof require !== 'undefined') XLSX = require('xlsx');
/* output format determined by filename */
XLSX.writeFile(workbook, 'out.xlsb');
/* at this point, out.xlsb is a file that you can distribute */
```
Browser add to web page (click to show)
The `sheet_to_html` utility function generates HTML code that can be added to
any DOM element.
```js
var worksheet = workbook.Sheets[workbook.SheetNames[0]];
var container = document.getElementById('tableau');
container.innerHTML = XLSX.utils.sheet_to_html(worksheet);
```
Browser save file (click to show)
Note: browser generates binary blob and forces a "download" to client. This
example uses [FileSaver](https://github.com/eligrey/FileSaver.js/):
```js
/* bookType can be any supported output type */
var wopts = { bookType:'xlsx', bookSST:false, type:'binary' };
var wbout = XLSX.write(workbook,wopts);
function s2ab(s) {
var buf = new ArrayBuffer(s.length);
var view = new Uint8Array(buf);
for (var i=0; i!=s.length; ++i) view[i] = s.charCodeAt(i) & 0xFF;
return buf;
}
/* the saveAs call downloads a file on the local machine */
saveAs(new Blob([s2ab(wbout)],{type:"application/octet-stream"}), "test.xlsx");
```
Browser upload to server (click to show)
A complete example using XHR is [included in the XHR demo](demos/xhr/), along
with examples for fetch and wrapper libraries. This example assumes the server
can handle Base64-encoded files (see the demo for a basic nodejs server):
```js
/* in this example, send a base64 string to the server */
var wopts = { bookType:'xlsx', bookSST:false, type:'base64' };
var wbout = XLSX.write(workbook,wopts);
var req = new XMLHttpRequest();
req.open("POST", "/upload", true);
var formdata = new FormData();
formdata.append('file', 'test.xlsx'); // <-- server expects `file` to hold name
formdata.append('data', wbout); // <-- `data` holds the base64-encoded data
req.send(formdata);
```
### Writing Examples
- exporting an HTML table
- generates a simple file
### Streaming Write
The streaming write functions are available in the `XLSX.stream` object. They
take the same arguments as the normal write functions but return a Readable
Stream. They are only exposed in NodeJS.
- `XLSX.stream.to_csv` is the streaming version of `XLSX.utils.sheet_to_csv`.
- `XLSX.stream.to_html` is the streaming version of `XLSX.utils.sheet_to_html`.
nodejs convert to CSV and write file (click to show)
```js
var output_file_name = "out.csv";
var stream = XLSX.stream.to_csv(worksheet);
stream.pipe(fs.createWriteStream(output_file_name));
```
pipes write streams to nodejs response.
## Interface
`XLSX` is the exposed variable in the browser and the exported node variable
`XLSX.version` is the version of the library (added by the build script).
`XLSX.SSF` is an embedded version of the [format library](http://git.io/ssf).
### Parsing functions
`XLSX.read(data, read_opts)` attempts to parse `data`.
`XLSX.readFile(filename, read_opts)` attempts to read `filename` and parse.
Parse options are described in the [Parsing Options](#parsing-options) section.
### Writing functions
`XLSX.write(wb, write_opts)` attempts to write the workbook `wb`
`XLSX.writeFile(wb, filename, write_opts)` attempts to write `wb` to `filename`
`XLSX.writeFileAsync(filename, wb, o, cb)` attempts to write `wb` to `filename`.
If `o` is omitted, the writer will use the third argument as the callback.
`XLSX.stream` contains a set of streaming write functions.
Write options are described in the [Writing Options](#writing-options) section.
### Utilities
Utilities are available in the `XLSX.utils` object and are described in the
[Utility Functions](#utility-functions) section:
**Importing:**
- `aoa_to_sheet` converts an array of arrays of JS data to a worksheet.
- `json_to_sheet` converts an array of JS objects to a worksheet.
- `table_to_sheet` converts a DOM TABLE element to a worksheet.
**Exporting:**
- `sheet_to_json` converts a worksheet object to an array of JSON objects.
- `sheet_to_csv` generates delimiter-separated-values output.
- `sheet_to_html` generates HTML output.
- `sheet_to_formulae` generates a list of the formulae (with value fallbacks).
**Cell and cell address manipulation:**
- `format_cell` generates the text value for a cell (using number formats).
- `encode_row / decode_row` converts between 0-indexed rows and 1-indexed rows.
- `encode_col / decode_col` converts between 0-indexed columns and column names.
- `encode_cell / decode_cell` converts cell addresses.
- `encode_range / decode_range` converts cell ranges.
## Common Spreadsheet Format
js-xlsx conforms to the Common Spreadsheet Format (CSF):
### General Structures
Cell address objects are stored as `{c:C, r:R}` where `C` and `R` are 0-indexed
column and row numbers, respectively. For example, the cell address `B5` is
represented by the object `{c:1, r:4}`.
Cell range objects are stored as `{s:S, e:E}` where `S` is the first cell and
`E` is the last cell in the range. The ranges are inclusive. For example, the
range `A3:B7` is represented by the object `{s:{c:0, r:2}, e:{c:1, r:6}}`.
Utility functions perform a row-major order walk traversal of a sheet range:
```js
for(var R = range.s.r; R <= range.e.r; ++R) {
for(var C = range.s.c; C <= range.e.c; ++C) {
var cell_address = {c:C, r:R};
/* if an A1-style address is needed, encode the address */
var cell_ref = XLSX.utils.encode_cell(cell_address);
}
}
```
### Cell Object
| Key | Description |
| --- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `v` | raw value (see Data Types section for more info) |
| `w` | formatted text (if applicable) |
| `t` | cell type: `b` Boolean, `n` Number, `e` error, `s` String, `d` Date |
| `f` | cell formula encoded as an A1-style string (if applicable) |
| `F` | range of enclosing array if formula is array formula (if applicable) |
| `r` | rich text encoding (if applicable) |
| `h` | HTML rendering of the rich text (if applicable) |
| `c` | comments associated with the cell |
| `z` | number format string associated with the cell (if requested) |
| `l` | cell hyperlink object (`.Target` holds link, `.Tooltip` is tooltip) |
| `s` | the style/theme of the cell (if applicable) |
Built-in export utilities (such as the CSV exporter) will use the `w` text if it
is available. To change a value, be sure to delete `cell.w` (or set it to
`undefined`) before attempting to export. The utilities will regenerate the `w`
text from the number format (`cell.z`) and the raw value if possible.
The actual array formula is stored in the `f` field of the first cell in the
array range. Other cells in the range will omit the `f` field.
#### Data Types
The raw value is stored in the `v` field, interpreted based on the `t` field.
Type `b` is the Boolean type. `v` is interpreted according to JS truth tables.
Type `e` is the Error type. `v` holds the number and `w` holds the common name:
Error values and interpretation (click to show)
| Value | Error Meaning |
| -----: | :-------------- |
| `0x00` | `#NULL!` |
| `0x07` | `#DIV/0!` |
| `0x0F` | `#VALUE!` |
| `0x17` | `#REF!` |
| `0x1D` | `#NAME?` |
| `0x24` | `#NUM!` |
| `0x2A` | `#N/A` |
| `0x2B` | `#GETTING_DATA` |
Type `n` is the Number type. This includes all forms of data that Excel stores
as numbers, such as dates/times and Boolean fields. Excel exclusively uses data
that can be fit in an IEEE754 floating point number, just like JS Number, so the
`v` field holds the raw number. The `w` field holds formatted text. Dates are
stored as numbers by default and converted with `XLSX.SSF.parse_date_code`.
Type `d` is the Date type, generated only when the option `cellDates` is passed.
Since JSON does not have a natural Date type, parsers are generally expected to
store ISO 8601 Date strings like you would get from `date.toISOString()`. On
the other hand, writers and exporters should be able to handle date strings and
JS Date objects. Note that Excel disregards timezone modifiers and treats all
dates in the local timezone. js-xlsx does not correct for this error.
Type `s` is the String type. `v` should be explicitly stored as a string to
avoid possible confusion.
Type `z` represents blank stub cells. These do not have any data or type, and
are not processed by any of the core library functions. By default these cells
will not be generated; the parser `sheetStubs` option must be set to `true`.
#### Dates
Excel Date Code details (click to show)
By default, Excel stores dates as numbers with a format code that specifies date
processing. For example, the date `19-Feb-17` is stored as the number `42785`
with a number format of `d-mmm-yy`. The `SSF` module understands number formats
and performs the appropriate conversion.
XLSX also supports a special date type `d` where the data is an ISO 8601 date
string. The formatter converts the date back to a number.
The default behavior for all parsers is to generate number cells. Setting
`cellDates` to true will force the generators to store dates.
Time Zones and Dates (click to show)
Excel has no native concept of universal time. All times are specified in the
local time zone. Excel limitations prevent specifying true absolute dates.
Following Excel, this library treats all dates as relative to local time zone.
Epochs: 1900 and 1904 (click to show)
Excel supports two epochs (January 1 1900 and January 1 1904), see
["1900 vs. 1904 Date System" article](http://support2.microsoft.com/kb/180162).
The workbook's epoch can be determined by examining the workbook's
`wb.Workbook.WBProps.date1904` property:
```js
!!(((wb.Workbook||{}).WBProps||{}).date1904)
```
### Sheet Objects
Each key that does not start with `!` maps to a cell (using `A-1` notation)
`sheet[address]` returns the cell object for the specified address.
**Special sheet keys (accessible as `sheet[key]`, each starting with `!`):**
- `sheet['!ref']`: A-1 based range representing the sheet range. Functions that
work with sheets should use this parameter to determine the range. Cells that
are assigned outside of the range are not processed. In particular, when
writing a sheet by hand, cells outside of the range are not included
Functions that handle sheets should test for the presence of `!ref` field.
If the `!ref` is omitted or is not a valid range, functions are free to treat
the sheet as empty or attempt to guess the range. The standard utilities that
ship with this library treat sheets as empty (for example, the CSV output is
empty string).
When reading a worksheet with the `sheetRows` property set, the ref parameter
will use the restricted range. The original range is set at `ws['!fullref']`
- `sheet['!margins']`: Object representing the page margins. The default values
follow Excel's "normal" preset. Excel also has a "wide" and a "narrow" preset
but they are stored as raw measurements. The main properties are listed below:
Page margin details (click to show)
| key | description | "normal" | "wide" | "narrow" |
|----------|------------------------|:---------|:-------|:-------- |
| `left` | left margin (inches) | `0.7` | `1.0` | `0.25` |
| `right` | right margin (inches) | `0.7` | `1.0` | `0.25` |
| `top` | top margin (inches) | `0.75` | `1.0` | `0.75` |
| `bottom` | bottom margin (inches) | `0.75` | `1.0` | `0.75` |
| `header` | header margin (inches) | `0.3` | `0.5` | `0.3` |
| `footer` | footer margin (inches) | `0.3` | `0.5` | `0.3` |
```js
/* Set worksheet sheet to "normal" */
ws["!margins"]={left:0.7, right:0.7, top:0.75,bottom:0.75,header:0.3,footer:0.3}
/* Set worksheet sheet to "wide" */
ws["!margins"]={left:1.0, right:1.0, top:1.0, bottom:1.0, header:0.5,footer:0.5}
/* Set worksheet sheet to "narrow" */
ws["!margins"]={left:0.25,right:0.25,top:0.75,bottom:0.75,header:0.3,footer:0.3}
```
#### Worksheet Object
In addition to the base sheet keys, worksheets also add:
- `ws['!cols']`: array of column properties objects. Column widths are actually
stored in files in a normalized manner, measured in terms of the "Maximum
Digit Width" (the largest width of the rendered digits 0-9, in pixels). When
parsed, the column objects store the pixel width in the `wpx` field, character
width in the `wch` field, and the maximum digit width in the `MDW` field.
- `ws['!rows']`: array of row properties objects as explained later in the docs.
Each row object encodes properties including row height and visibility.
- `ws['!merges']`: array of range objects corresponding to the merged cells in
the worksheet. Plain text formats do not support merge cells. CSV export
will write all cells in the merge range if they exist, so be sure that only
the first cell (upper-left) in the range is set.
- `ws['!protect']`: object of write sheet protection properties. The `password`
key specifies the password for formats that support password-protected sheets
(XLSX/XLSB/XLS). The writer uses the XOR obfuscation method. The following
keys control the sheet protection -- set to `false` to enable a feature when
sheet is locked or set to `true` to disable a feature:
Worksheet Protection Details (click to show)
| key | feature (true=disabled / false=enabled) | default |
|:----------------------|:----------------------------------------|:-----------|
| `selectLockedCells` | Select locked cells | enabled |
| `selectUnlockedCells` | Select unlocked cells | enabled |
| `formatCells` | Format cells | disabled |
| `formatColumns` | Format columns | disabled |
| `formatRows` | Format rows | disabled |
| `insertColumns` | Insert columns | disabled |
| `insertRows` | Insert rows | disabled |
| `insertHyperlinks` | Insert hyperlinks | disabled |
| `deleteColumns` | Delete columns | disabled |
| `deleteRows` | Delete rows | disabled |
| `sort` | Sort | disabled |
| `autoFilter` | Filter | disabled |
| `pivotTables` | Use PivotTable reports | disabled |
| `objects` | Edit objects | enabled |
| `scenarios` | Edit scenarios | enabled |
- `ws['!autofilter']`: AutoFilter object following the schema:
```typescript
type AutoFilter = {
ref:string; // A-1 based range representing the AutoFilter table range
}
```
#### Chartsheet Object
Chartsheets are represented as standard sheets. They are distinguished with the
`!type` property set to `"chart"`.
The underlying data and `!ref` refer to the cached data in the chartsheet. The
first row of the chartsheet is the underlying header.
#### Macrosheet Object
Macrosheets are represented as standard sheets. They are distinguished with the
`!type` property set to `"macro"`.
#### Dialogsheet Object
Dialogsheets are represented as standard sheets. They are distinguished with the
`!type` property set to `"dialog"`.
### Workbook Object
`workbook.SheetNames` is an ordered list of the sheets in the workbook
`wb.Sheets[sheetname]` returns an object representing the worksheet.
`wb.Props` is an object storing the standard properties. `wb.Custprops` stores
custom properties. Since the XLS standard properties deviate from the XLSX
standard, XLS parsing stores core properties in both places.
`wb.Workbook` stores [workbook-level attributes](#workbook-level-attributes).
#### Workbook File Properties
The various file formats use different internal names for file properties. The
workbook `Props` object normalizes the names:
File Properties (click to show)
| JS Name | Excel Description |
|:--------------|:-------------------------------|
| `Title` | Summary tab "Title" |
| `Subject` | Summary tab "Subject" |
| `Author` | Summary tab "Author" |
| `Manager` | Summary tab "Manager" |
| `Company` | Summary tab "Company" |
| `Category` | Summary tab "Category" |
| `Keywords` | Summary tab "Keywords" |
| `Comments` | Summary tab "Comments" |
| `LastAuthor` | Statistics tab "Last saved by" |
| `CreatedDate` | Statistics tab "Created" |
For example, to set the workbook title property:
```js
if(!wb.Props) wb.Props = {};
wb.Props.Title = "Insert Title Here";
```
Custom properties are added in the workbook `Custprops` object:
```js
if(!wb.Custprops) wb.Custprops = {};
wb.Custprops["Custom Property"] = "Custom Value";
```
Writers will process the `Props` key of the options object:
```js
/* force the Author to be "SheetJS" */
XLSX.write(wb, {Props:{Author:"SheetJS"}});
```
### Workbook-Level Attributes
`wb.Workbook` stores workbook-level attributes.
#### Defined Names
`wb.Workbook.Names` is an array of defined name objects which have the keys:
Defined Name Properties (click to show)
| Key | Description |
|:----------|:-----------------------------------------------------------------|
| `Sheet` | Name scope. Sheet Index (0 = first sheet) or `null` (Workbook) |
| `Name` | Case-sensitive name. Standard rules apply ** |
| `Ref` | A1-style Reference (`"Sheet1!$A$1:$D$20"`) |
| `Comment` | Comment (only applicable for XLS/XLSX/XLSB) |
Excel allows two sheet-scoped defined names to share the same name. However, a
sheet-scoped name cannot collide with a workbook-scope name. Workbook writers
may not enforce this constraint.
#### Miscellaneous Workbook Properties
`wb.Workbook.WBProps` holds other workbook properties:
| Key | Description |
|:----------------|:----------------------------------------------------|
| `date1904` | epoch: 0/false for 1900 system, 1/true for 1904 |
| `filterPrivacy` | Warn or strip personally identifying info on save |
### Document Features
Even for basic features like date storage, the official Excel formats store the
same content in different ways. The parsers are expected to convert from the
underlying file format representation to the Common Spreadsheet Format. Writers
are expected to convert from CSF back to the underlying file format.
#### Formulae
The A1-style formula string is stored in the `f` field. Even though different
file formats store the formulae in different ways, the formats are translated.
Even though some formats store formulae with a leading equal sign, CSF formulae
do not start with `=`.
Representation of A1=1, A2=2, A3=A1+A2 (click to show)
```js
{
"!ref": "A1:A3",
A1: { t:'n', v:1 },
A2: { t:'n', v:2 },
A3: { t:'n', v:3, f:'A1+A2' }
}
```
Shared formulae are decompressed and each cell has the formula corresponding to
its cell. Writers generally do not attempt to generate shared formulae.
Cells with formula entries but no value will be serialized in a way that Excel
and other spreadsheet tools will recognize. This library will not automatically
compute formula results! For example, to compute `BESSELJ` in a worksheet:
Formula without known value (click to show)
```js
{
"!ref": "A1:A3",
A1: { t:'n', v:3.14159 },
A2: { t:'n', v:2 },
A3: { t:'n', f:'BESSELJ(A1,A2)' }
}
```
**Array Formulae**
Array formulae are stored in the top-left cell of the array block. All cells
of an array formula have a `F` field corresponding to the range. A single-cell
formula can be distinguished from a plain formula by the presence of `F` field.
Array Formula examples (click to show)
For example, setting the cell `C1` to the array formula `{=SUM(A1:A3*B1:B3)}`:
```js
worksheet['C1'] = { t:'n', f: "SUM(A1:A3*B1:B3)", F:"C1:C1" };
```
For a multi-cell array formula, every cell has the same array range but only the
first cell specifies the formula. Consider `D1:D3=A1:A3*B1:B3`:
```js
worksheet['D1'] = { t:'n', F:"D1:D3", f:"A1:A3*B1:B3" };
worksheet['D2'] = { t:'n', F:"D1:D3" };
worksheet['D3'] = { t:'n', F:"D1:D3" };
```
Utilities and writers are expected to check for the presence of a `F` field and
ignore any possible formula element `f` in cells other than the starting cell.
They are not expected to perform validation of the formulae!
Formula Output Utility Function (click to show)
The `sheet_to_formulae` method generates one line per formula or array formula.
Array formulae are rendered in the form `range=formula` while plain cells are
rendered in the form `cell=formula or value`. Note that string literals are
prefixed with an apostrophe `'`, consistent with Excel's formula bar display.
Formulae File Format Details (click to show)
| Storage Representation | Formats | Read | Write |
|:-----------------------|:-------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|
| A1-style strings | XLSX | :o: | :o: |
| RC-style strings | XLML and plain text | :o: | :o: |
| BIFF Parsed formulae | XLSB and all XLS formats | :o: | |
| OpenFormula formulae | ODS/FODS/UOS | :o: | :o: |
Since Excel prohibits named cells from colliding with names of A1 or RC style
cell references, a (not-so-simple) regex conversion is possible. BIFF Parsed
formulae have to be explicitly unwound. OpenFormula formulae can be converted
with regular expressions.
#### Column Properties
The `!cols` array in each worksheet, if present, is a collection of `ColInfo`
objects which have the following properties:
```typescript
type ColInfo = {
/* visibility */
hidden?: boolean; // if true, the column is hidden
/* column width is specified in one of the following ways: */
wpx?: number; // width in screen pixels
width?: number; // width in Excel's "Max Digit Width", width*256 is integral
wch?: number; // width in characters
/* other fields for preserving features from files */
MDW?: number; // Excel's "Max Digit Width" unit, always integral
};
```
Why are there three width types? (click to show)
There are three different width types corresponding to the three different ways
spreadsheets store column widths:
SYLK and other plain text formats use raw character count. Contemporaneous tools
like Visicalc and Multiplan were character based. Since the characters had the
same width, it sufficed to store a count. This tradition was continued into the
BIFF formats.
SpreadsheetML (2003) tried to align with HTML by standardizing on screen pixel
count throughout the file. Column widths, row heights, and other measures use
pixels. When the pixel and character counts do not align, Excel rounds values.
XLSX internally stores column widths in a nebulous "Max Digit Width" form. The
Max Digit Width is the width of the largest digit when rendered (generally the
"0" character is the widest). The internal width must be an integer multiple of
the the width divided by 256. ECMA-376 describes a formula for converting
between pixels and the internal width. This represents a hybrid approach.
Read functions attempt to populate all three properties. Write functions will
try to cycle specified values to the desired type. In order to avoid potential
conflicts, manipulation should delete the other properties first. For example,
when changing the pixel width, delete the `wch` and `width` properties.
Implementation details (click to show)
Given the constraints, it is possible to determine the MDW without actually
inspecting the font! The parsers guess the pixel width by converting from width
to pixels and back, repeating for all possible MDW and selecting the MDW that
minimizes the error. XLML actually stores the pixel width, so the guess works
in the opposite direction.
Even though all of the information is made available, writers are expected to
follow the priority order:
1) use `width` field if available
2) use `wpx` pixel width if available
3) use `wch` character count if available
#### Row Properties
The `!rows` array in each worksheet, if present, is a collection of `RowInfo`
objects which have the following properties:
```typescript
type RowInfo = {
/* visibility */
hidden?: boolean; // if true, the row is hidden
/* row height is specified in one of the following ways: */
hpx?: number; // height in screen pixels
hpt?: number; // height in points
level?: number; // 0-indexed outline / group level
};
```
Note: Excel UI displays the base outline level as `1` and the max level as `8`.
The `level` field stores the base outline as `0` and the max level as `7`.
Implementation details (click to show)
Excel internally stores row heights in points. The default resolution is 72 DPI
or 96 PPI, so the pixel and point size should agree. For different resolutions
they may not agree, so the library separates the concepts.
Even though all of the information is made available, writers are expected to
follow the priority order:
1) use `hpx` pixel height if available
2) use `hpt` point height if available
#### Number Formats
The `cell.w` formatted text for each cell is produced from `cell.v` and `cell.z`
format. If the format is not specified, the Excel `General` format is used.
The format can either be specified as a string or as an index into the format
table. Parsers are expected to populate `workbook.SSF` with the number format
table. Writers are expected to serialize the table.
Custom tools should ensure that the local table has each used format string
somewhere in the table. Excel convention mandates that the custom formats start
at index 164. The following example creates a custom format from scratch:
New worksheet with custom format (click to show)
```js
var wb = {
SheetNames: ["Sheet1"],
Sheets: {
Sheet1: {
"!ref":"A1:C1",
A1: { t:"n", v:10000 }, // <-- General format
B1: { t:"n", v:10000, z: "0%" }, // <-- Builtin format
C1: { t:"n", v:10000, z: "\"T\"\ #0.00" } // <-- Custom format
}
}
}
```
The rules are slightly different from how Excel displays custom number formats.
In particular, literal characters must be wrapped in double quotes or preceded
by a backslash. For more info, see the Excel documentation article
`Create or delete a custom number format` or ECMA-376 18.8.31 (Number Formats)
Default Number Formats (click to show)
The default formats are listed in ECMA-376 18.8.30:
| ID | Format |
|---:|:---------------------------|
| 0 | `General` |
| 1 | `0` |
| 2 | `0.00` |
| 3 | `#,##0` |
| 4 | `#,##0.00` |
| 9 | `0%` |
| 10 | `0.00%` |
| 11 | `0.00E+00` |
| 12 | `# ?/?` |
| 13 | `# ??/??` |
| 14 | `m/d/yy` (see below) |
| 15 | `d-mmm-yy` |
| 16 | `d-mmm` |
| 17 | `mmm-yy` |
| 18 | `h:mm AM/PM` |
| 19 | `h:mm:ss AM/PM` |
| 20 | `h:mm` |
| 21 | `h:mm:ss` |
| 22 | `m/d/yy h:mm` |
| 37 | `#,##0 ;(#,##0)` |
| 38 | `#,##0 ;[Red](#,##0)` |
| 39 | `#,##0.00;(#,##0.00)` |
| 40 | `#,##0.00;[Red](#,##0.00)` |
| 45 | `mm:ss` |
| 46 | `[h]:mm:ss` |
| 47 | `mmss.0` |
| 48 | `##0.0E+0` |
| 49 | `@` |
Format 14 (`m/d/yy`) is localized by Excel: even though the file specifies that
number format, it will be drawn differently based on system settings. It makes
sense when the producer and consumer of files are in the same locale, but that
is not always the case over the Internet. To get around this ambiguity, parse
functions accept the `dateNF` option to override the interpretation of that
specific format string.
#### Hyperlinks
Hyperlinks are stored in the `l` key of cell objects. The `Target` field of the
hyperlink object is the target of the link, including the URI fragment. Tooltips
are stored in the `Tooltip` field and are displayed when you move your mouse
over the text.
For example, the following snippet creates a link from cell `A3` to
with the tip `"Find us @ SheetJS.com!"`:
```js
ws['A3'].l = { Target:"http://sheetjs.com", Tooltip:"Find us @ SheetJS.com!" };
```
Note that Excel does not automatically style hyperlinks -- they will generally
be displayed as normal text.
#### Cell Comments
Cell comments are objects stored in the `c` array of cell objects. The actual
contents of the comment are split into blocks based on the comment author. The
`a` field of each comment object is the author of the comment and the `t` field
is the plain text representation.
For example, the following snippet appends a cell comment into cell `A1`:
```js
if(!ws.A1.c) ws.A1.c = [];
ws.A1.c.push({a:"SheetJS", t:"I'm a little comment, short and stout!"});
```
Note: XLSB enforces a 54 character limit on the Author name. Names longer than
54 characters may cause issues with other formats.
#### Sheet Visibility
Excel enables hiding sheets in the lower tab bar. The sheet data is stored in
the file but the UI does not readily make it available. Standard hidden sheets
are revealed in the "Unhide" menu. Excel also has "very hidden" sheets which
cannot be revealed in the menu. It is only accessible in the VB Editor!
The visibility setting is stored in the `Hidden` property of sheet props array.
More details (click to show)
| Value | Definition |
|:-----:|:------------|
| 0 | Visible |
| 1 | Hidden |
| 2 | Very Hidden |
With :
```js
> wb.Workbook.Sheets.map(function(x) { return [x.name, x.Hidden] })
[ [ 'Visible', 0 ], [ 'Hidden', 1 ], [ 'VeryHidden', 2 ] ]
```
Non-Excel formats do not support the Very Hidden state. The best way to test
if a sheet is visible is to check if the `Hidden` property is logical truth:
```js
> wb.Workbook.Sheets.map(function(x) { return [x.name, !x.Hidden] })
[ [ 'Visible', true ], [ 'Hidden', false ], [ 'VeryHidden', false ] ]
```
#### VBA and Macros
VBA Macros are stored in a special data blob that is exposed in the `vbaraw`
property of the workbook object when the `bookVBA` option is `true`. They are
supported in `XLSM`, `XLSB`, and `BIFF8 XLS` formats. The `XLSM` and `XLSB`
writers automatically insert the data blobs if it is present in the workbook.
Macrosheets (click to show)
Older versions of Excel also supported a non-VBA "macrosheet" sheet type that
stored automation commands. These are exposed in objects with the `!type`
property set to `"macro"`.
Detecting macros in workbooks (click to show)
The `vbaraw` field will only be set if macros are present, so testing is simple:
```js
function wb_has_macro(wb/*:workbook*/)/*:boolean*/ {
if(!!wb.vbaraw) return true;
const sheets = wb.SheetNames.map((n) => wb.Sheets[n]);
return sheets.some((ws) => !!ws && ws['!type']=='macro');
}
```
## Parsing Options
The exported `read` and `readFile` functions accept an options argument:
| Option Name | Default | Description |
| :---------- | ------: | :--------------------------------------------------- |
|`type` | | Input data encoding (see Input Type below) |
|`raw` | false | If true, plain text parsing will not parse values ** |
|`cellFormula`| true | Save formulae to the .f field |
|`cellHTML` | true | Parse rich text and save HTML to the `.h` field |
|`cellNF` | false | Save number format string to the `.z` field |
|`cellStyles` | false | Save style/theme info to the `.s` field |
|`cellText` | true | Generated formatted text to the `.w` field |
|`cellDates` | false | Store dates as type `d` (default is `n`) |
|`dateNF` | | If specified, use the string for date code 14 ** |
|`sheetStubs` | false | Create cell objects of type `z` for stub cells |
|`sheetRows` | 0 | If >0, read the first `sheetRows` rows ** |
|`bookDeps` | false | If true, parse calculation chains |
|`bookFiles` | false | If true, add raw files to book object ** |
|`bookProps` | false | If true, only parse enough to get book metadata ** |
|`bookSheets` | false | If true, only parse enough to get the sheet names |
|`bookVBA` | false | If true, copy VBA blob to `vbaraw` field ** |
|`password` | "" | If defined and file is encrypted, use password ** |
|`WTF` | false | If true, throw errors on unexpected file features ** |
- Even if `cellNF` is false, formatted text will be generated and saved to `.w`
- In some cases, sheets may be parsed even if `bookSheets` is false.
- Excel aggressively tries to interpret values from CSV and other plain text.
This leads to surprising behavior! The `raw` option suppresses value parsing.
- `bookSheets` and `bookProps` combine to give both sets of information
- `Deps` will be an empty object if `bookDeps` is false
- `bookFiles` behavior depends on file type:
* `keys` array (paths in the ZIP) for ZIP-based formats
* `files` hash (mapping paths to objects representing the files) for ZIP
* `cfb` object for formats using CFB containers
- `sheetRows-1` rows will be generated when looking at the JSON object output
(since the header row is counted as a row when parsing the data)
- `bookVBA` merely exposes the raw VBA CFB object. It does not parse the data.
XLSM and XLSB store the VBA CFB object in `xl/vbaProject.bin`. BIFF8 XLS mixes
the VBA entries alongside the core Workbook entry, so the library generates a
new XLSB-compatible blob from the XLS CFB container.
- Currently only XOR encryption is supported. Unsupported error will be thrown
for files employing other encryption methods.
- WTF is mainly for development. By default, the parser will suppress read
errors on single worksheets, allowing you to read from the worksheets that do
parse properly. Setting `WTF:1` forces those errors to be thrown.
### Input Type
Strings can be interpreted in multiple ways. The `type` parameter for `read`
tells the library how to parse the data argument:
| `type` | expected input |
|------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|
| `"base64"` | string: Base64 encoding of the file |
| `"binary"` | string: binary string (byte `n` is `data.charCodeAt(n)`) |
| `"string"` | string: JS string (characters interpreted as UTF8) |
| `"buffer"` | nodejs Buffer |
| `"array"` | array: array of 8-bit unsigned int (byte `n` is `data[n]`) |
| `"file"` | string: path of file that will be read (nodejs only) |
### Guessing File Type
Implementation Details (click to show)
Excel and other spreadsheet tools read the first few bytes and apply other
heuristics to determine a file type. This enables file type punning: renaming
files with the `.xls` extension will tell your computer to use Excel to open the
file but Excel will know how to handle it. This library applies similar logic:
| Byte 0 | Raw File Type | Spreadsheet Types |
|:-------|:--------------|:----------------------------------------------------|
| `0xD0` | CFB Container | BIFF 5/8 or password-protected XLSX/XLSB or WQ3/QPW |
| `0x09` | BIFF Stream | BIFF 2/3/4/5 |
| `0x3C` | XML/HTML | SpreadsheetML / Flat ODS / UOS1 / HTML / plain text |
| `0x50` | ZIP Archive | XLSB or XLSX/M or ODS or UOS2 or plain text |
| `0x49` | Plain Text | SYLK or plain text |
| `0x54` | Plain Text | DIF or plain text |
| `0xEF` | UTF8 Encoded | SpreadsheetML / Flat ODS / UOS1 / HTML / plain text |
| `0xFF` | UTF16 Encoded | SpreadsheetML / Flat ODS / UOS1 / HTML / plain text |
| `0x00` | Record Stream | Lotus WK\* or Quattro Pro or plain text |
| `0x7B` | Plain text | RTF or plain text |
| `0x0A` | Plain text | SpreadsheetML / Flat ODS / UOS1 / HTML / plain text |
| `0x0D` | Plain text | SpreadsheetML / Flat ODS / UOS1 / HTML / plain text |
| `0x20` | Plain text | SpreadsheetML / Flat ODS / UOS1 / HTML / plain text |
DBF files are detected based on the first byte as well as the third and fourth
bytes (corresponding to month and day of the file date)
Plain text format guessing follows the priority order:
| Format | Test |
|:-------|:--------------------------------------------------------------------|
| XML | `
Why are random text files valid? (click to show)
Excel is extremely aggressive in reading files. Adding an XLS extension to any
display text file (where the only characters are ANSI display chars) tricks
Excel into thinking that the file is potentially a CSV or TSV file, even if it
is only one column! This library attempts to replicate that behavior.
The best approach is to validate the desired worksheet and ensure it has the
expected number of rows or columns. Extracting the range is extremely simple:
```js
var range = XLSX.utils.decode_range(worksheet['!ref']);
var ncols = range.e.c - range.r.c + 1, nrows = range.e.r - range.s.r + 1;
```
## Writing Options
The exported `write` and `writeFile` functions accept an options argument:
| Option Name | Default | Description |
| :---------- | -------: | :-------------------------------------------------- |
|`type` | | Output data encoding (see Output Type below) |
|`cellDates` | `false` | Store dates as type `d` (default is `n`) |
|`bookSST` | `false` | Generate Shared String Table ** |
|`bookType` | `"xlsx"` | Type of Workbook (see below for supported formats) |
|`sheet` | `""` | Name of Worksheet for single-sheet formats ** |
|`compression`| `false` | Use ZIP compression for ZIP-based formats ** |
|`Props` | | Override workbook properties when writing ** |
|`themeXLSX` | | Override theme XML when writing XLSX/XLSB/XLSM ** |
- `bookSST` is slower and more memory intensive, but has better compatibility
with older versions of iOS Numbers
- The raw data is the only thing guaranteed to be saved. Features not described
in this README may not be serialized.
- `cellDates` only applies to XLSX output and is not guaranteed to work with
third-party readers. Excel itself does not usually write cells with type `d`
so non-Excel tools may ignore the data or error in the presence of dates.
- `Props` is an object mirroring the workbook `Props` field. See the table from
the [Workbook File Properties](#workbook-file-properties) section.
- if specified, the string from `themeXLSX` will be saved as the primary theme
for XLSX/XLSB/XLSM files (to `xl/theme/theme1.xml` in the ZIP)
### Supported Output Formats
For broad compatibility with third-party tools, this library supports many
output formats. The specific file type is controlled with `bookType` option:
| `bookType` | file ext | container | sheets | Description |
| :--------- | -------: | :-------: | :----- |:------------------------------- |
| `xlsx` | `.xlsx` | ZIP | multi | Excel 2007+ XML Format |
| `xlsm` | `.xlsm` | ZIP | multi | Excel 2007+ Macro XML Format |
| `xlsb` | `.xlsb` | ZIP | multi | Excel 2007+ Binary Format |
| `biff8` | `.xls` | CFB | multi | Excel 97-2004 Workbook Format |
| `biff5` | `.xls` | CFB | multi | Excel 5.0/95 Workbook Format |
| `biff2` | `.xls` | none | single | Excel 2.0 Worksheet Format |
| `xlml` | `.xls` | none | multi | Excel 2003-2004 (SpreadsheetML) |
| `ods` | `.ods` | ZIP | multi | OpenDocument Spreadsheet |
| `fods` | `.fods` | none | multi | Flat OpenDocument Spreadsheet |
| `csv` | `.csv` | none | single | Comma Separated Values |
| `txt` | `.txt` | none | single | UTF-16 Unicode Text (TXT) |
| `sylk` | `.sylk` | none | single | Symbolic Link (SYLK) |
| `html` | `.html` | none | single | HTML Document |
| `dif` | `.dif` | none | single | Data Interchange Format (DIF) |
| `rtf` | `.rtf` | none | single | Rich Text Format (RTF) |
| `prn` | `.prn` | none | single | Lotus Formatted Text |
- `compression` only applies to formats with ZIP containers.
- Formats that only support a single sheet require a `sheet` option specifying
the worksheet. If the string is empty, the first worksheet is used.
- `writeFile` will automatically guess the output file format based on the file
extension if `bookType` is not specified. It will choose the first format in
the aforementioned table that matches the extension.
### Output Type
The `type` argument for `write` mirrors the `type` argument for `read`:
| `type` | output |
|------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|
| `"base64"` | string: Base64 encoding of the file |
| `"binary"` | string: binary string (byte `n` is `data.charCodeAt(n)`) |
| `"string"` | string: JS string (characters interpreted as UTF8) |
| `"buffer"` | nodejs Buffer |
| `"file"` | string: path of file that will be created (nodejs only) |
## Utility Functions
The `sheet_to_*` functions accept a worksheet and an optional options object.
The `*_to_sheet` functions accept a data object and an optional options object.
The examples are based on the following worksheet:
```
XXX| A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
1 | S | h | e | e | t | J | S |
2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
```
### Array of Arrays Input
`XLSX.utils.aoa_to_sheet` takes an array of arrays of JS values and returns a
worksheet resembling the input data. Numbers, Booleans and Strings are stored
as the corresponding styles. Dates are stored as date or numbers. Array holes
and explicit `undefined` values are skipped. `null` values may be stubbed. All
other values are stored as strings. The function takes an options argument:
| Option Name | Default | Description |
| :---------- | :------: | :-------------------------------------------------- |
|`dateNF` | FMT 14 | Use specified date format in string output |
|`cellDates` | false | Store dates as type `d` (default is `n`) |
|`sheetStubs` | false | Create cell objects of type `z` for `null` values |
Examples (click to show)
To generate the example sheet:
```js
var ws = XLSX.utils.aoa_to_sheet([
"SheetJS".split(""),
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7],
[2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
]);
```
### Array of Objects Input
`XLSX.utils.json_to_sheet` takes an array of objects and returns a worksheet
with automatically-generated "headers" based on the keys of the objects. The
default column order is determined by the first appearance of the field using
`Object.keys`, but can be overridden using the options argument:
| Option Name | Default | Description |
| :---------- | :------: | :-------------------------------------------------- |
|`header` | | Use specified column order (default `Object.keys`) |
|`dateNF` | FMT 14 | Use specified date format in string output |
|`cellDates` | false | Store dates as type `d` (default is `n`) |
Examples (click to show)
The original sheet cannot be reproduced because JS object keys must be unique.
After replacing the second `e` and `S` with `e_1` and `S_1`:
```js
var ws = XLSX.utils.json_to_sheet([
{S:1,h:2,e:3,e_1:4,t:5,J:6,S_1:7},
{S:2,h:3,e:4,e_1:5,t:6,J:7,S_1:8}
], {header:["S","h","e","e_1","t","J","S_1"]});
```
### HTML Table Input
`XLSX.utils.table_to_sheet` takes a table DOM element and returns a worksheet
resembling the input table. Numbers are parsed. All other data will be stored
as strings.
`XLSX.utils.table_to_book` produces a minimal workbook based on the worksheet.
Both functions accept options arguments:
| Option Name | Default | Description |
| :---------- | :------: | :-------------------------------------------------- |
|`dateNF` | FMT 14 | Use specified date format in string output |
|`cellDates` | false | Store dates as type `d` (default is `n`) |
|`raw` | | If true, every cell will hold raw strings |
Examples (click to show)
To generate the example sheet, start with the HTML table:
```html
```
To process the table:
```js
var tbl = document.getElementById('sheetjs');
var wb = XLSX.utils.table_to_book(tbl);
```
Note: `XLSX.read` can handle HTML represented as strings.
### Formulae Output
`XLSX.utils.sheet_to_formulae` generates an array of commands that represent
how a person would enter data into an application. Each entry is of the form
`A1-cell-address=formula-or-value`. String literals are prefixed with a `'` in
accordance with Excel.
Examples (click to show)
For the example sheet:
```js
> var o = XLSX.utils.sheet_to_formulae(ws);
> o.filter(function(v, i) { return i % 5 === 0; });
[ 'A1=\'S', 'F1=\'J', 'D2=4', 'B3=3', 'G3=8' ]
```
### Delimiter-Separated Output
As an alternative to the `writeFile` CSV type, `XLSX.utils.sheet_to_csv` also
produces CSV output. The function takes an options argument:
| Option Name | Default | Description |
| :---------- | :------: | :-------------------------------------------------- |
|`FS` | `","` | "Field Separator" delimiter between fields |
|`RS` | `"\n"` | "Record Separator" delimiter between rows |
|`dateNF` | FMT 14 | Use specified date format in string output |
|`strip` | false | Remove trailing field separators in each record ** |
|`blankrows` | true | Include blank lines in the CSV output |
|`skipHidden` | false | Skips hidden rows/columns in the CSV output |
- `strip` will remove trailing commas from each line under default `FS/RS`
- `blankrows` must be set to `false` to skip blank lines.
Examples (click to show)
For the example sheet:
```js
> console.log(XLSX.utils.sheet_to_csv(ws));
S,h,e,e,t,J,S
1,2,3,4,5,6,7
2,3,4,5,6,7,8
> console.log(XLSX.utils.sheet_to_csv(ws, {FS:"\t"}));
S h e e t J S
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2 3 4 5 6 7 8
> console.log(XLSX.utils.sheet_to_csv(ws,{FS:":",RS:"|"}));
S:h:e:e:t:J:S|1:2:3:4:5:6:7|2:3:4:5:6:7:8|
```
#### UTF-16 Unicode Text
The `txt` output type uses the tab character as the field separator. If the
`codepage` library is available (included in full distribution but not core),
the output will be encoded in `CP1200` and the BOM will be prepended.
### HTML Output
As an alternative to the `writeFile` HTML type, `XLSX.utils.sheet_to_html` also
produces HTML output. The function takes an options argument:
| Option Name | Default | Description |
| :---------- | :------: | :-------------------------------------------------- |
|`editable` | false | If true, set `contenteditable="true"` for every TD |
|`header` | | Override header (default `html body`) |
|`footer` | | Override footer (default `/body /html`) |
Examples (click to show)
For the example sheet:
```js
> console.log(XLSX.utils.sheet_to_html(ws));
// ...
```
### JSON
`XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json` generates different types of JS objects. The function
takes an options argument:
| Option Name | Default | Description |
| :---------- | :------: | :-------------------------------------------------- |
|`raw` | `false` | Use raw values (true) or formatted strings (false) |
|`range` | from WS | Override Range (see table below) |
|`header` | | Control output format (see table below) |
|`dateNF` | FMT 14 | Use specified date format in string output |
|`defval` | | Use specified value in place of null or undefined |
|`blankrows` | ** | Include blank lines in the output ** |
- `raw` only affects cells which have a format code (`.z`) field or a formatted
text (`.w`) field.
- If `header` is specified, the first row is considered a data row; if `header`
is not specified, the first row is the header row and not considered data.
- When `header` is not specified, the conversion will automatically disambiguate
header entries by affixing `_` and a count starting at `1`. For example, if
three columns have header `foo` the output fields are `foo`, `foo_1`, `foo_2`
- `null` values are returned when `raw` is true but are skipped when false.
- If `defval` is not specified, null and undefined values are skipped normally.
If specified, all null and undefined points will be filled with `defval`
- When `header` is `1`, the default is to generate blank rows. `blankrows` must
be set to `false` to skip blank rows.
- When `header` is not `1`, the default is to skip blank rows. `blankrows` must
be true to generate blank rows
`range` is expected to be one of:
| `range` | Description |
| :--------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------- |
| (number) | Use worksheet range but set starting row to the value |
| (string) | Use specified range (A1-style bounded range string) |
| (default) | Use worksheet range (`ws['!ref']`) |
`header` is expected to be one of:
| `header` | Description |
| :--------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------- |
| `1` | Generate an array of arrays ("2D Array") |
| `"A"` | Row object keys are literal column labels |
| array of strings | Use specified strings as keys in row objects |
| (default) | Read and disambiguate first row as keys |
If header is not `1`, the row object will contain the non-enumerable property
`__rowNum__` that represents the row of the sheet corresponding to the entry.
Examples (click to show)
For the example sheet:
```js
> XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json(ws);
[ { S: 1, h: 2, e: 3, e_1: 4, t: 5, J: 6, S_1: 7 },
{ S: 2, h: 3, e: 4, e_1: 5, t: 6, J: 7, S_1: 8 } ]
> XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json(ws, {header:"A"});
[ { A: 'S', B: 'h', C: 'e', D: 'e', E: 't', F: 'J', G: 'S' },
{ A: '1', B: '2', C: '3', D: '4', E: '5', F: '6', G: '7' },
{ A: '2', B: '3', C: '4', D: '5', E: '6', F: '7', G: '8' } ]
> XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json(ws, {header:["A","E","I","O","U","6","9"]});
[ { '6': 'J', '9': 'S', A: 'S', E: 'h', I: 'e', O: 'e', U: 't' },
{ '6': '6', '9': '7', A: '1', E: '2', I: '3', O: '4', U: '5' },
{ '6': '7', '9': '8', A: '2', E: '3', I: '4', O: '5', U: '6' } ]
> XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json(ws, {header:1});
[ [ 'S', 'h', 'e', 'e', 't', 'J', 'S' ],
[ '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7' ],
[ '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8' ] ]
```
Example showing the effect of `raw`:
```js
> ws['A2'].w = "3"; // set A2 formatted string value
> XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json(ws, {header:1});
[ [ 'S', 'h', 'e', 'e', 't', 'J', 'S' ],
[ '3', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7' ], // <-- A2 uses the formatted string
[ '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8' ] ]
> XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json(ws, {header:1, raw:true});
[ [ 'S', 'h', 'e', 'e', 't', 'J', 'S' ],
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ], // <-- A2 uses the raw value
[ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 ] ]
```
## File Formats
Despite the library name `xlsx`, it supports numerous spreadsheet file formats:
| Format | Read | Write |
|:-------------------------------------------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|
| **Excel Worksheet/Workbook Formats** |:-----:|:-----:|
| Excel 2007+ XML Formats (XLSX/XLSM) | :o: | :o: |
| Excel 2007+ Binary Format (XLSB BIFF12) | :o: | :o: |
| Excel 2003-2004 XML Format (XML "SpreadsheetML") | :o: | :o: |
| Excel 97-2004 (XLS BIFF8) | :o: | :o: |
| Excel 5.0/95 (XLS BIFF5) | :o: | :o: |
| Excel 4.0 (XLS/XLW BIFF4) | :o: | |
| Excel 3.0 (XLS BIFF3) | :o: | |
| Excel 2.0/2.1 (XLS BIFF2) | :o: | :o: |
| **Excel Supported Text Formats** |:-----:|:-----:|
| Delimiter-Separated Values (CSV/TXT) | :o: | :o: |
| Data Interchange Format (DIF) | :o: | :o: |
| Symbolic Link (SYLK/SLK) | :o: | :o: |
| Lotus Formatted Text (PRN) | :o: | :o: |
| UTF-16 Unicode Text (TXT) | :o: | :o: |
| **Other Workbook/Worksheet Formats** |:-----:|:-----:|
| OpenDocument Spreadsheet (ODS) | :o: | :o: |
| Flat XML ODF Spreadsheet (FODS) | :o: | :o: |
| Uniform Office Format Spreadsheet (标文通 UOS1/UOS2) | :o: | |
| dBASE II/III/IV / Visual FoxPro (DBF) | :o: | |
| Lotus 1-2-3 (WKS/WK1/WK2/WK3/WK4/123) | :o: | |
| Quattro Pro Spreadsheet (WQ1/WQ2/WB1/WB2/WB3/QPW) | :o: | |
| **Other Common Spreadsheet Output Formats** |:-----:|:-----:|
| HTML Tables | :o: | :o: |
| Rich Text Format tables (RTF) | | :o: |
### Excel 2007+ XML (XLSX/XLSM)
(click to show)
XLSX and XLSM files are ZIP containers containing a series of XML files in
accordance with the Open Packaging Conventions (OPC). The XLSM format, almost
identical to XLSX, is used for files containing macros.
The format is standardized in ECMA-376 and later in ISO/IEC 29500. Excel does
not follow the specification, and there are additional documents discussing how
Excel deviates from the specification.
### Excel 2.0-95 (BIFF2/BIFF3/BIFF4/BIFF5)
(click to show)
BIFF 2/3 XLS are single-sheet streams of binary records. Excel 4 introduced
the concept of a workbook (`XLW` files) but also had single-sheet `XLS` format.
The structure is largely similar to the Lotus 1-2-3 file formats. BIFF5/8/12
extended the format in various ways but largely stuck to the same record format.
There is no official specification for any of these formats. Excel 95 can write
files in these formats, so record lengths and fields were determined by writing
in all of the supported formats and comparing files. Excel 2016 can generate
BIFF5 files, enabling a full suite of file tests starting from XLSX or BIFF2.
### Excel 97-2004 Binary (BIFF8)
(click to show)
BIFF8 exclusively uses the Compound File Binary container format, splitting some
content into streams within the file. At its core, it still uses an extended
version of the binary record format from older versions of BIFF.
The `MS-XLS` specification covers the basics of the file format, and other
specifications expand on serialization of features like properties.
### Excel 2003-2004 (SpreadsheetML)
(click to show)
Predating XLSX, SpreadsheetML files are simple XML files. There is no official
and comprehensive specification, although MS has released documentation on the
format. Since Excel 2016 can generate SpreadsheetML files, mapping features is
pretty straightforward.
### Excel 2007+ Binary (XLSB, BIFF12)
(click to show)
Introduced in parallel with XLSX, the XLSB format combines the BIFF architecture
with the content separation and ZIP container of XLSX. For the most part nodes
in an XLSX sub-file can be mapped to XLSB records in a corresponding sub-file.
The `MS-XLSB` specification covers the basics of the file format, and other
specifications expand on serialization of features like properties.
### Delimiter-Separated Values (CSV/TXT)
(click to show)
Excel CSV deviates from RFC4180 in a number of important ways. The generated
CSV files should generally work in Excel although they may not work in RFC4180
compatible readers. The parser should generally understand Excel CSV. The
writer proactively generates cells for formulae if values are unavailable.
Excel TXT uses tab as the delimiter and code page 1200.
Notes:
- Like in Excel, files starting with `0x49 0x44 ("ID")` are treated as Symbolic
Link files. Unlike Excel, if the file does not have a valid SYLK header, it
will be proactively reinterpreted as CSV. There are some files with semicolon
delimiter that align with a valid SYLK file. For the broadest compatibility,
all cells with the value of `ID` are automatically wrapped in double-quotes.
### Other Workbook Formats
(click to show)
Support for other formats is generally far XLS/XLSB/XLSX support, due in large
part to a lack of publicly available documentation. Test files were produced in
the respective apps and compared to their XLS exports to determine structure.
The main focus is data extraction.
#### Lotus 1-2-3 (WKS/WK1/WK2/WK3/WK4/123)
(click to show)
The Lotus formats consist of binary records similar to the BIFF structure. Lotus
did release a specification decades ago covering the original WK1 format. Other
features were deduced by producing files and comparing to Excel support.
#### Quattro Pro (WQ1/WQ2/WB1/WB2/WB3/QPW)
(click to show)
The Quattro Pro formats use binary records in the same way as BIFF and Lotus.
Some of the newer formats (namely WB3 and QPW) use a CFB enclosure just like
BIFF8 XLS.
#### OpenDocument Spreadsheet (ODS/FODS)
(click to show)
ODS is an XML-in-ZIP format akin to XLSX while FODS is an XML format akin to
SpreadsheetML. Both are detailed in the OASIS standard, but tools like LO/OO
add undocumented extensions. The parsers and writers do not implement the full
standard, instead focusing on parts necessary to extract and store raw data.
#### Uniform Office Spreadsheet (UOS1/2)
(click to show)
UOS is a very similar format, and it comes in 2 varieties corresponding to ODS
and FODS respectively. For the most part, the difference between the formats
is in the names of tags and attributes.
### Other Single-Worksheet Formats
Many older formats supported only one worksheet:
#### dBASE and Visual FoxPro (DBF)
(click to show)
DBF is really a typed table format: each column can only hold one data type and
each record omits type information. The parser generates a header row and
inserts records starting at the second row of the worksheet.
Multi-file extensions like external memos and tables are currently unsupported,
limited by the general ability to read arbitrary files in the web browser.
#### Symbolic Link (SYLK)
(click to show)
There is no real documentation. All knowledge was gathered by saving files in
various versions of Excel to deduce the meaning of fields. Notes:
- Plain formulae are stored in the RC form.
- Column widths are rounded to integral characters.
#### Lotus Formatted Text (PRN)
(click to show)
There is no real documentation, and in fact Excel treats PRN as an output-only
file format. Nevertheless we can guess the column widths and reverse-engineer
the original layout. Excel's 240 character width limitation is not enforced.
#### Data Interchange Format (DIF)
(click to show)
There is no unified definition. Visicalc DIF differs from Lotus DIF, and both
differ from Excel DIF. Where ambiguous, the parser/writer follows the expected
behavior from Excel. In particular, Excel extends DIF in incompatible ways:
- Since Excel automatically converts numbers-as-strings to numbers, numeric
string constants are converted to formulae: `"0.3" -> "=""0.3""`
- DIF technically expects numeric cells to hold the raw numeric data, but Excel
permits formatted numbers (including dates)
- DIF technically has no support for formulae, but Excel will automatically
convert plain formulae. Array formulae are not preserved.
#### HTML
(click to show)
Excel HTML worksheets include special metadata encoded in styles. For example,
`mso-number-format` is a localized string containing the number format. Despite
the metadata the output is valid HTML, although it does accept bare `&` symbols.
#### Rich Text Format (RTF)
(click to show)
Excel RTF worksheets are stored in clipboard when copying cells or ranges from a
worksheet. The supported codes are a subset of the Word RTF support.
## Testing
### Node
(click to show)
`make test` will run the node-based tests. By default it runs tests on files in
every supported format. To test a specific file type, set `FMTS` to the format
you want to test. Feature-specific tests are available with `make test_misc`
```bash
$ make test_misc # run core tests
$ make test # run full tests
$ make test_xls # only use the XLS test files
$ make test_xlsx # only use the XLSX test files
$ make test_xlsb # only use the XLSB test files
$ make test_xml # only use the XML test files
$ make test_ods # only use the ODS test files
```
To enable all errors, set the environment variable `WTF=1`:
```bash
$ make test # run full tests
$ WTF=1 make test # enable all error messages
```
`flow` and `eslint` checks are available:
```bash
$ make lint # eslint checks
$ make flow # make lint + Flow checking
$ make tslint # check TS definitions
```
### Browser
(click to show)
The core in-browser tests are available at `tests/index.html` within this repo.
Start a local server and navigate to that directory to run the tests.
`make ctestserv` will start a server on port 8000.
`make ctest` will generate the browser fixtures. To add more files, edit the
`tests/fixtures.lst` file and add the paths.
To run the full in-browser tests, clone the repo for
[`oss.sheetjs.com`](https://github.com/SheetJS/SheetJS.github.io) and replace
the `xlsx.js` file (then open a browser window and go to `stress.html`):
```bash
$ cp xlsx.js ../SheetJS.github.io
$ cd ../SheetJS.github.io
$ simplehttpserver # or "python -mSimpleHTTPServer" or "serve"
$ open -a Chromium.app http://localhost:8000/stress.html
```
### Tested Environments
(click to show)
- NodeJS `0.8`, `0.10`, `0.12`, `4.x`, `5.x`, `6.x`, `7.x`, `8.x`
- IE 6/7/8/9/10/11 (IE 6-9 require shims)
- Chrome 24+ (including Android 4.0+)
- Safari 6+ (iOS and Desktop)
- Edge 13+, FF 18+, and Opera 12+
Tests utilize the mocha testing framework. Travis-CI and Sauce Labs links:
- for XLSX module in nodejs
- for XLSX module in nodejs
- for XLS\* modules
- for XLS\* modules using Sauce Labs
The Travis-CI test suite also includes tests for various time zones. To change
the timezone locally, set the TZ environment variable:
```bash
$ env TZ="Asia/Kolkata" WTF=1 make test_misc
```
### Test Files
Test files are housed in [another repo](https://github.com/SheetJS/test_files).
Running `make init` will refresh the `test_files` submodule and get the files.
Note that this requires `svn`, `git`, `hg` and other commands that may not be
available. If `make init` fails, please download the latest version of the test
files snapshot from [the repo](https://github.com/SheetJS/test_files/releases)
Latest Snapshot (click to show)
Latest test files snapshot:
(download and unzip to the `test_files` subdirectory)
## Contributing
Due to the precarious nature of the Open Specifications Promise, it is very
important to ensure code is cleanroom. [Contribution Notes](CONTRIBUTING.md)
File organization (click to show)
At a high level, the final script is a concatenation of the individual files in
the `bits` folder. Running `make` should reproduce the final output on all
platforms. The README is similarly split into bits in the `docbits` folder.
Folders:
| folder | contents |
|:-------------|:--------------------------------------------------------------|
| `bits` | raw source files that make up the final script |
| `docbits` | raw markdown files that make up `README.md` |
| `bin` | server-side bin scripts (`xlsx.njs`) |
| `dist` | dist files for web browsers and nonstandard JS environments |
| `demos` | demo projects for platforms like ExtendScript and Webpack |
| `tests` | browser tests (run `make ctest` to rebuild) |
| `types` | typescript definitions and tests |
| `misc` | miscellaneous supporting scripts |
| `test_files` | test files (pulled from the test files repository) |
After cloning the repo, running `make help` will display a list of commands.
### OSX/Linux
(click to show)
The `xlsx.js` file is constructed from the files in the `bits` subdirectory. The
build script (run `make`) will concatenate the individual bits to produce the
script. Before submitting a contribution, ensure that running make will produce
the `xlsx.js` file exactly. The simplest way to test is to add the script:
```bash
$ git add xlsx.js
$ make clean
$ make
$ git diff xlsx.js
```
To produce the dist files, run `make dist`. The dist files are updated in each
version release and *should not be committed between versions*.
### Windows
(click to show)
The included `make.cmd` script will build `xlsx.js` from the `bits` directory.
Building is as simple as:
```cmd
> make
```
To prepare development environment:
```cmd
> make init
```
The full list of commands available in Windows are displayed in `make help`:
```
make init -- install deps and global modules
make lint -- run eslint linter
make test -- run mocha test suite
make misc -- run smaller test suite
make book -- rebuild README and summary
make help -- display this message
```
### Tests
(click to show)
The `test_misc` target (`make test_misc` on Linux/OSX / `make misc` on Windows)
runs the targeted feature tests. It should take 5-10 seconds to perform feature
tests without testing against the entire test battery. New features should be
accompanied with tests for the relevant file formats and features.
For tests involving the read side, an appropriate feature test would involve
reading an existing file and checking the resulting workbook object. If a
parameter is involved, files should be read with different values to verify that
the feature is working as expected.
For tests involving a new write feature which can already be parsed, appropriate
feature tests would involve writing a workbook with the feature and then opening
and verifying that the feature is preserved.
For tests involving a new write feature without an existing read ability, please
add a feature test to the kitchen sink `tests/write.js`.
## License
Please consult the attached LICENSE file for details. All rights not explicitly
granted by the Apache 2.0 License are reserved by the Original Author.
## References
OSP-covered Specifications (click to show)
- `MS-CFB`: Compound File Binary File Format
- `MS-CTXLS`: Excel Custom Toolbar Binary File Format
- `MS-EXSPXML3`: Excel Calculation Version 2 Web Service XML Schema
- `MS-ODATA`: Open Data Protocol (OData)
- `MS-ODRAW`: Office Drawing Binary File Format
- `MS-ODRAWXML`: Office Drawing Extensions to Office Open XML Structure
- `MS-OE376`: Office Implementation Information for ECMA-376 Standards Support
- `MS-OFFCRYPTO`: Office Document Cryptography Structure
- `MS-OI29500`: Office Implementation Information for ISO/IEC 29500 Standards Support
- `MS-OLEDS`: Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) Data Structures
- `MS-OLEPS`: Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) Property Set Data Structures
- `MS-OODF3`: Office Implementation Information for ODF 1.2 Standards Support
- `MS-OSHARED`: Office Common Data Types and Objects Structures
- `MS-OVBA`: Office VBA File Format Structure
- `MS-XLDM`: Spreadsheet Data Model File Format
- `MS-XLS`: Excel Binary File Format (.xls) Structure Specification
- `MS-XLSB`: Excel (.xlsb) Binary File Format
- `MS-XLSX`: Excel (.xlsx) Extensions to the Office Open XML SpreadsheetML File Format
- `XLS`: Microsoft Office Excel 97-2007 Binary File Format Specification
- `RTF`: Rich Text Format
- ISO/IEC 29500:2012(E) "Information technology — Document description and processing languages — Office Open XML File Formats"
- Open Document Format for Office Applications Version 1.2 (29 September 2011)
- Worksheet File Format (From Lotus) December 1984